Introduction
Social Media Misinformation Statistics: Social media has become the primary public space of the current era because it defines public opinion and creates discussions that shape economic growth. The world faces its most difficult challenge because the same internet connection that brings people together to build their social networks creates the problem of false information.
The speed of false information distribution has reached new heights because algorithms, AI creation tools, and human psychology work together to spread political, health, financial, and global crisis false narratives. The report combines current social media misinformation statistics with economic impact to explain the 2025 misinformation crisis, which includes its effects on society and the economy.
Editor’s Choice
- TikTok users from 27% of its 2025 users find it hard to determine trustworthy news sources, which makes TikTok the most difficult platform to use.
- Google Search leads in trust, with 60% of users saying it is easy to find reliable information.
- 54% of U.S. adults now get news from social media at least occasionally, embedding platforms into daily news habits.
- Facebook (33%) and YouTube (32%) remain the top social platforms for news consumption in the U.S.
- 61% of adults aged 65+ struggle to consistently identify false content online.
- Teenagers (13–17) saw a 24% increase in misinformation exposure, driven by meme-based formats.
- College-educated users are 30% more likely to question misleading content than non-degree holders.
- 64% of people say fake news causes major confusion about current events.
- The digital devices of 60% of Americans serve as their main news source, which increases their chance of encountering false information.
- Misinformation on X experienced a 240% increase during the period leading up to Election Day in the 2024 U.S. elections.
- Social media platforms of Meta shared health-related hoaxes, which reached a total of 9 million shares during the year 2025.
- The study found that 47% of misinformation during crises originates from users who create fake accounts and automated systems.
- The countries of Tunisia and Lebanon, which represent developing markets, experience more than 75% of their population facing exposure to false information.
- Misinformation content receives 64% of its total user interaction through algorithmic systems, which operate across digital platforms.
- The worldwide economic impact of social media platforms spreading false information reached a total of 89 billion dollars during the year 2025.
How Users Perceive Trust And Misinformation Across Major Digital Platforms
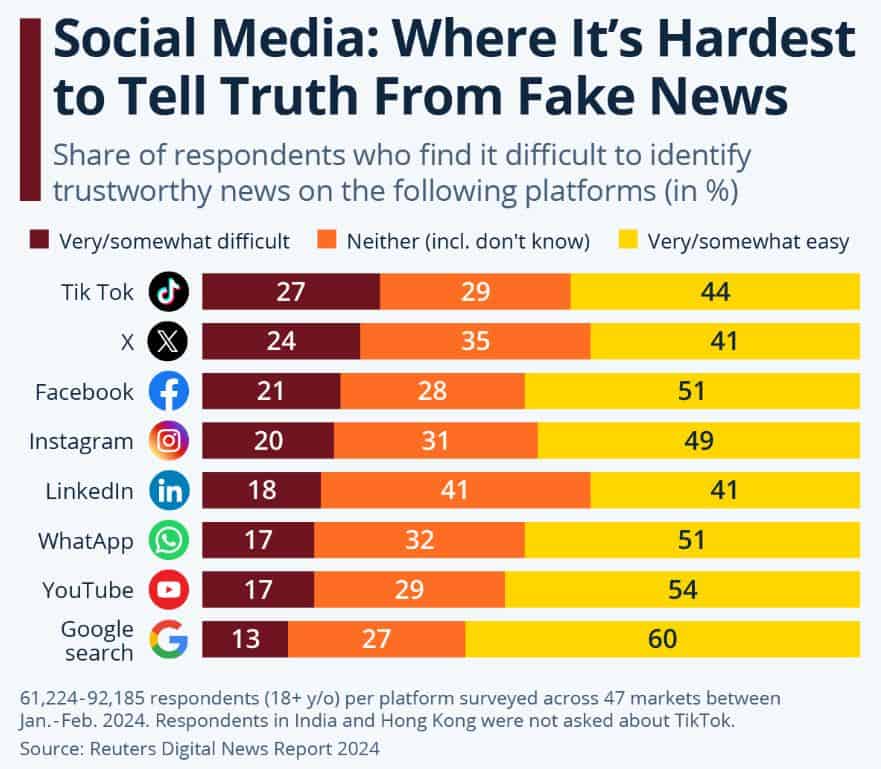
(Source: statista.com)
- The 2025 data highlights clear differences in how users experience social media misinformation across platforms.
- The TikTok platform represents the most challenging space because 27% of its users find it hard to identify reliable news sources.
- The X platform, which previously operated as Twitter, shows a close similarity because 24% of users experience difficulties, and 35% of users show uncertain behavior without confidence.
- The study found that approximately 20 to 21% of users face challenges, yet almost half of all users succeed in establishing credibility assessment.
- Users on LinkedIn display neutral behavior because 41% of users show no trust or distrust toward shared content.
- Users on WhatsApp and YouTube experience difficulties at only 17% rate, while Google Search leads the way because 60% of users find trustworthy information with ease.
- The study results demonstrate how social media platforms spread false information through their specific system designs.
- The solution to reducing social media misinformation needs three elements, which include transparency, context, and advanced content moderation methods.
Social Media Became A Primary News Source For Americans
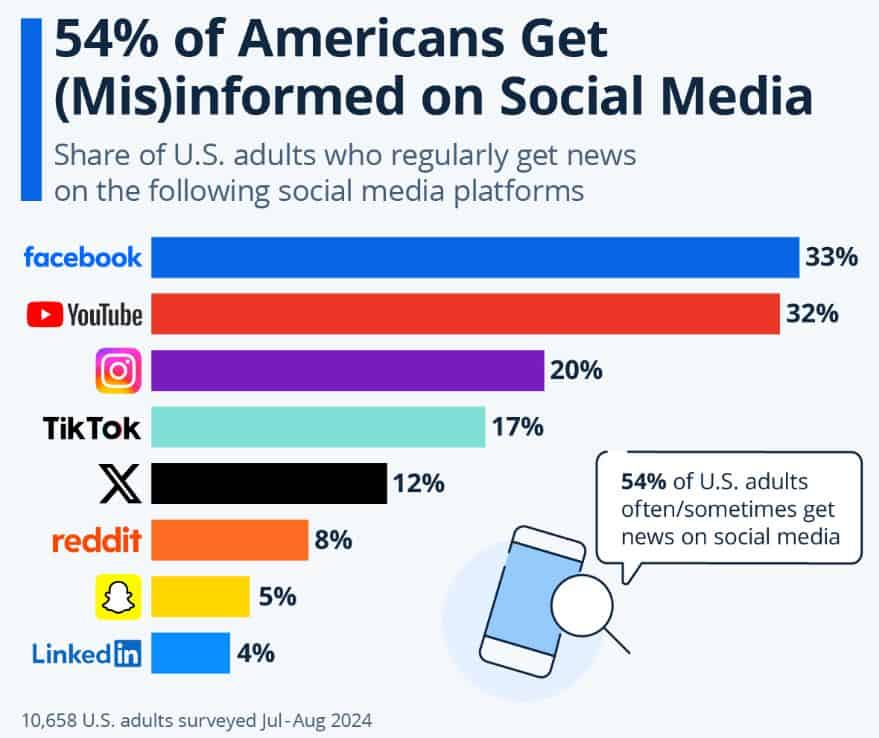
(Source: statista.com)
- According to a Statista report, the United States news environment experienced a major transformation, which the 2024 Pew research data demonstrates.
- American adults now access news through social media platforms, which they use at least sometimes despite ongoing worries about social media platforms spreading false information.
- The two leading news platforms, Facebook and YouTube, together account for 65 % of news consumption because their extensive audience base an/ their content recommendation /system drive viewer engagement.
- The top five platforms include Instagram, which has 20 % usage, and TikTok and X, both known for spreading false information.
- The trust dynamics present a more profound shift. Americans, especially young adults and Republicans, show increasing trust in social media news, which they associate with national news organizations.
- The pattern shows people choose social media platforms for their better content accessibility because they developed a fundamental distrust of traditional media.
- The use of algorithms in today’s political climate works to create social media content that presents known information to users.
- Social media misinformation transforms from a platform issue into a nationwide problem because people depend on social media platforms more than before.
- Social media platforms need to establish measurement systems to verify their news content while boosting public understanding of media content, which includes their news distribution methods.
Misinformation Exposure Varies Across Demographic Groups Online
- The 2025 data shows that social media misinformation affects users differently based on age, education, and context.
- The 65 age group represents the most vulnerable demographic because 61 % of older users cannot correctly identify false information.
- The exposure rate for teenagers aged 13 to 17 increased by 24 % because they interacted with meme content from TikTok and Snapchat.
- College-educated users show 30 % higher probability of distrust of false information than other educational groups.
- Rural users face double the risk of consuming false information because echo chambers develop in their communities.
- Adults between 30 and 45 years old show increasing trust in false financial information, while gender differences continue to exist.
- The two trends together demonstrate that social media platforms need special measures to stop people from spreading false information they trust because of their social media platforms.
Public Confusion And Shared Responsibility In the Fake News Landscape
- Social media misinformation shapes public understanding of current events, according to data that analysts use to study its effects.
- A striking 64% of people say fake news causes significant confusion, while another 24% experience moderate confusion—meaning nearly nine in ten people are affected in some way.
- Social media platforms need to handle their responsibility, according to 42% of respondents who believe that social media companies must stop false information from spreading.
- The public perceives prevention as a shared responsibility because 29% of people see platforms as partially accountable, while 31% of people see the public as responsible.
- Social media misinformation creates confusion between facts and opinions because users want to take action through critical thinking, governments need to enforce proper regulations, and platforms must develop new systems to prevent social media misinformation from spreading widely.
How Americans Are Shifting Their News Consumption Habits
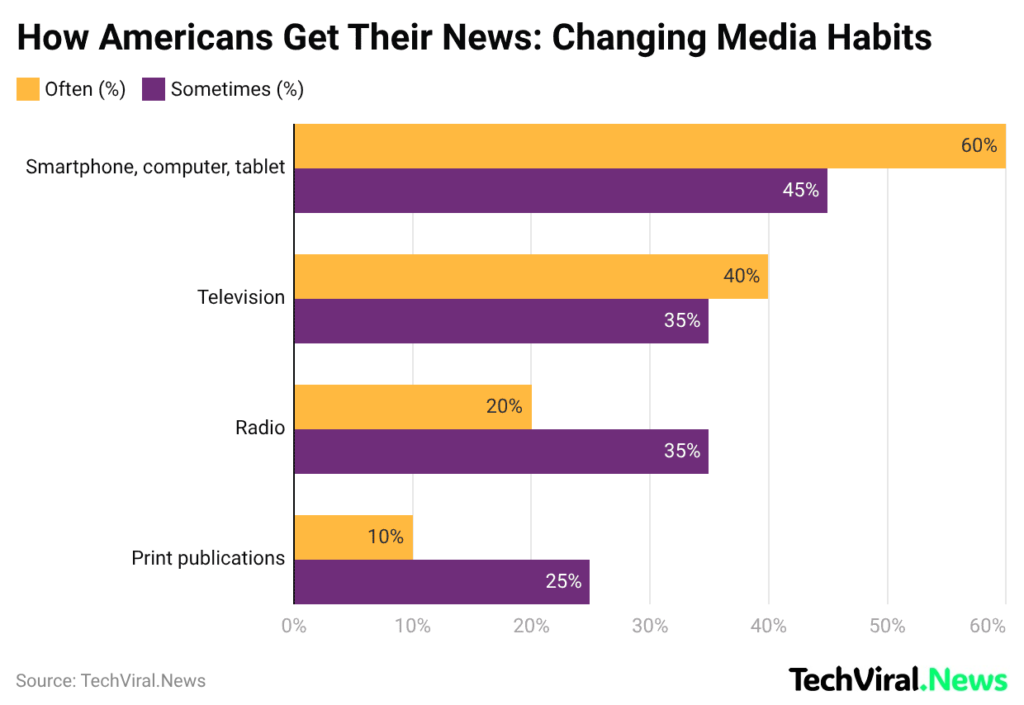
(Reference: sqmagazine.co.uk)
- According to SQ Magazine, US citizens now prefer to access news through digital platforms, according to the latest research data.
- 60% of Americans who use smartphones, computers, and tablets to access news, while 45% will use these devices to access news at times, which confirms that digital devices function as the main method people use to obtain news.
- Traditional television still matters, with 40% watching news often and 35% sometimes, but it now trails digital channels in daily relevance.
- Radio functions as a secondary medium because 20% of listeners use it frequently, while 35% of listeners use it at times.
- 10% of people read newspapers and magazines for news, while print media continues to decline.
- As people become more dependent on digital technology, their use of social media platforms leads to greater exposure to false information, which spreads through mobile devices.
- The current situation demonstrates that social media platforms now distribute false information to the public, which has become a major problem that determines how people understand information and trust media sources in a world where people access news through their mobile devices.
Misinformation Accelerates During Global Crises And Major Events
- Social media platforms use major global events as a weapon, which they employ to spread false information about current events.
- The 2024 U.S. elections saw a 240% increase in misinformation spread on X during the two days before Election Day, which demonstrated how political needs led to information distortion.
- Conflict zones show similar patterns—nearly 25% of social media users in Ukraine encountered state-sponsored disinformation, while the 2025 Israel–Gaza escalation triggered over 13,000 AI-generated visuals in a single week.
- Social media platforms have become the primary platform for misinformation which exists during periods of social unrest.
- The year 2025 saw nine million pandemic-related hoaxes spread across Meta platforms, while WhatsApp users shared false Marburg virus information, which created a 70% increase in chain messages that caused panic among people.
- The 2025 Atlantic hurricane season experienced a fourfold increase in eco-misinformation because climate disasters created more widespread problems.
- The enforcement process becomes difficult because 47% of crisis misinformation comes from either anonymous accounts or bot accounts.
- Social media misinformation operates through two main pathways, which show that uncertain situations require real-time solutions and emergency systems to stop non-trustworthy information from spreading during periods of low public confidence.
Research On False Information Distribution In Developing Countries
- Developing countries experience an excessive burden from social media false information because their mobile phone usage grows rapidly and their political situation remains unstable, while they lack proper content control systems for local languages.
- The information ecosystem in Tunisia and Lebanon demonstrates vulnerability because 78% and 76% of their population have access to misinformation, respectively.
- South Africa achieves the top position with a 36% rate of frequent exposure, which shows how people consume digital content throughout their everyday lives.
- The markets of Southeast Asia present high exposure rates, which exceed 68%, because both algorithms and influencer content control the spread of false information.
- India shows 55% overall platform exposure, yet its users encounter content 16% of the time because they either trust the platform more or face better user control systems.
- Latin American countries display mixed exposure patterns because Mexico shows the least exposure, from its 44% rate, yet 25% of people who encounter misinformation experience it frequently, which indicates that these people have stronger connections with the content.
Mental And Emotional Effects Of Repeated Exposure To False Information
- The psychological effects that social media misinformation causes to people now represent a concrete assessment that shows increasing damage to society, according to the analyst’s evaluation.
- The 2025 digital wellness survey found that 34% of users develop increased anxiety symptoms combined with decision-making difficulties after they see misleading information multiple times.
- Users who spent more than five hours on digital content daily showed 23% increased depressive symptoms, which established a direct relationship between content consumption and depressive symptoms.
- Health-related falsehoods caused stress because 18% of adults used self-diagnosis, while financial scams resulted in trust loss among 20% of users under 35.
- Gen Z appears particularly vulnerable because 41% of users now mistrust verified sources, which indicates a complete breakdown of trust in digital authority.
- Research studies show that reinforcement loops create stronger confirmation bias effects because users who study misinformation content display 28% lower trust scores.
- Social media misinformation creates a hidden mental health danger that requires platforms, policymakers, and users to solve before social media misinformation causes permanent harm to cognitive and emotional health.
How Platform Algorithms Intensify The Spread of False Content
- Platform algorithms function as potent creators that boost social media misinformation dissemination according to their current operational capabilities, which analysts observe.
- Algorithmic amplification accounted for 64% of total engagement with misinformation posts during 2025 because platforms create engineered reach, which differs from natural reach.
- Facebook’s recommender systems increased impressions of false and divisive content by 22%, while YouTube still surfaces one misleading video for every five watched, even in unpersonalized sessions.
- The velocity-first feed of TikTok enables false information to spread 15 % more easily because the platform emphasizes fast content delivery instead of fact-checking.
- The AI system of Instagram Reels creates personalized content, which resulted in a 31 % increase in political false information during the elections, while Twitter/X used hashtag clustering to make false stories become popular within minutes.
- The testing of friction layers on Reddit and other platforms leads to a real-time demotion of only 6 % of false content.
- Social media platforms will keep spreading false information until they change their algorithm because current systems let users engage with incorrect information, which creates widespread distribution of fake content.
The Rising Economic And Social Damage Caused By Misinformation
- The global cost of social media misinformation will reach US$ 89 billion in 2025 because of public health mistakes, election security expenses, and corporate reputation damages.
- The United States experienced US$ 4.2 billion in avoidable healthcare expenses between 2020 and 2025 because of COVID-related false narratives.
- The Financial markets experienced a 21 % increase in stock manipulation through misinformation, which resulted in US$ 2.3 billion in losses for retail investors during 2025.
- The financial danger for businesses has increased because 23 % of small businesses experience revenue declines because of fake reviews and local rumour campaigns.
- One in six PR agencies has started to provide misinformation monitoring as a main service, which shows how the industry has expanded.
- Social media misinformation causes financial damage, breaks trust, and stops lawmaking processes for seven different countries, and leads to digital burnout, which impacts almost 25% of knowledge workers.
New Global Actions Shaping The Fight Against Online Misinformation
- Social media platforms and institutional frameworks will begin their new response methods for handling social media misinformation in 2025 through a combination of artificial intelligence solutions and community duty.
- TikTok’s “Verified Voices” initiative, which started in April 2025, decreased misinformation distribution by 17%, which demonstrates that algorithm-based content selection affects overall content standards.
- Meta’s Horizon Guardian AI operates in virtual worlds to stop false information from spreading throughout the metaverse.
- X uses its Neural Trust credibility scoring system to measure user trust through their online activities, but this system has generated discussions about user data protection.
- WhatsApp uses language-model tagging to identify dangerous message sharing, while Reddit uses advanced moderator AI to enhance its community moderation process.
- The New York City alert system and Finnish and South Korean media literacy programs demonstrate how governments and educational institutions implement educational initiatives.
- The volume of social media misinformation maintains its high level, which demonstrates that technology needs continuing public involvement, together with regulatory frameworks, to achieve success against social media misinformation.
Conclusion
Social Media Misinformation Statistics: The 2025 data establishes one fact, which shows social media misinformation now operates as a global system that disturbs trust and human behavior and decision-making across the world. The platforms now control people who believe their content faster than institutions can respond to these platform operations, while algorithms create widespread uncertainty through their hidden activities. The statistics reveal a fragile information ecosystem—one where crises, demographics, and economic pressures accelerate the spread of false narratives. The data presents both challenges and opportunities for analysis.
Harmful effects can be decreased through better platform design, improved media literacy, and public-private partnerships. Social media has become the primary method for news consumption, which makes it essential to address social media misinformation as both a technical problem and a social duty, which will determine online trustworthiness in the forthcoming years.
FAQ
In 2025, TikTok and X rank highest for misinformation difficulty, while Google Search, YouTube, and WhatsApp are perceived as more trustworthy.
About 54% of U.S. adults get news from social media at least occasionally, with Facebook and YouTube leading usage.
Adults aged 65+ and teenagers (13–17) are the most vulnerable, with seniors struggling to identify false content and teens facing higher exposure.
Algorithms drive 64% of misinformation engagement by prioritizing viral and divisive content over verified accuracy.
Global losses reached an estimated US$ 89 billion in 2025, including healthcare waste, market manipulation, and business reputational damage.

