Introduction
Negative Effects of Technology Statistics: Technology is making everyday life easier, but it also includes several disadvantages. Many studies have reported concern about excessive screen time, particularly among teenagers, while many adolescents spend hours each day on social media and video platforms. It has been observed that using electronic devices at night, such as phones and laptops, can disrupt sleep.
On the other hand, in many workplaces, constant app notifications and messages often create stress, and due to these interruptions, an employee may lose focus and work less efficiently. Another serious concern is online safety, as data theft, hacking, and digital scams continue to increase. Health can also be affected by prolonged device use. When a person sits for too long, eye strain and neck or back pain may develop.
This article on the Negative Effects of technology statistics presents several statistical analyses and insights that will help you understand the negative impacts of technology and provide guidance on how technology should be used in a controlled and balanced way.
Editor’s Choice
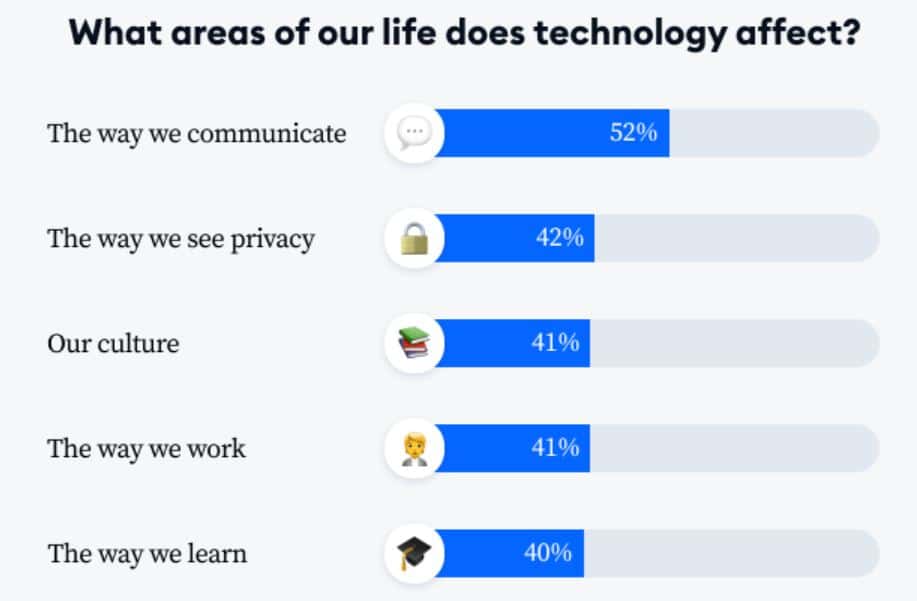
- As of 2025, the greatest negative impact is observed in communication, with 52% of participants reporting noticeable changes.
- A report published by Virtual Addiction further stated that people with internet addiction are 2.2 times more likely to suffer from sleep issues than non-addicted users.
- Constant digital distractions such as emails, notifications, and chat apps cost the U.S. economy approximately USD 650 billion annually.
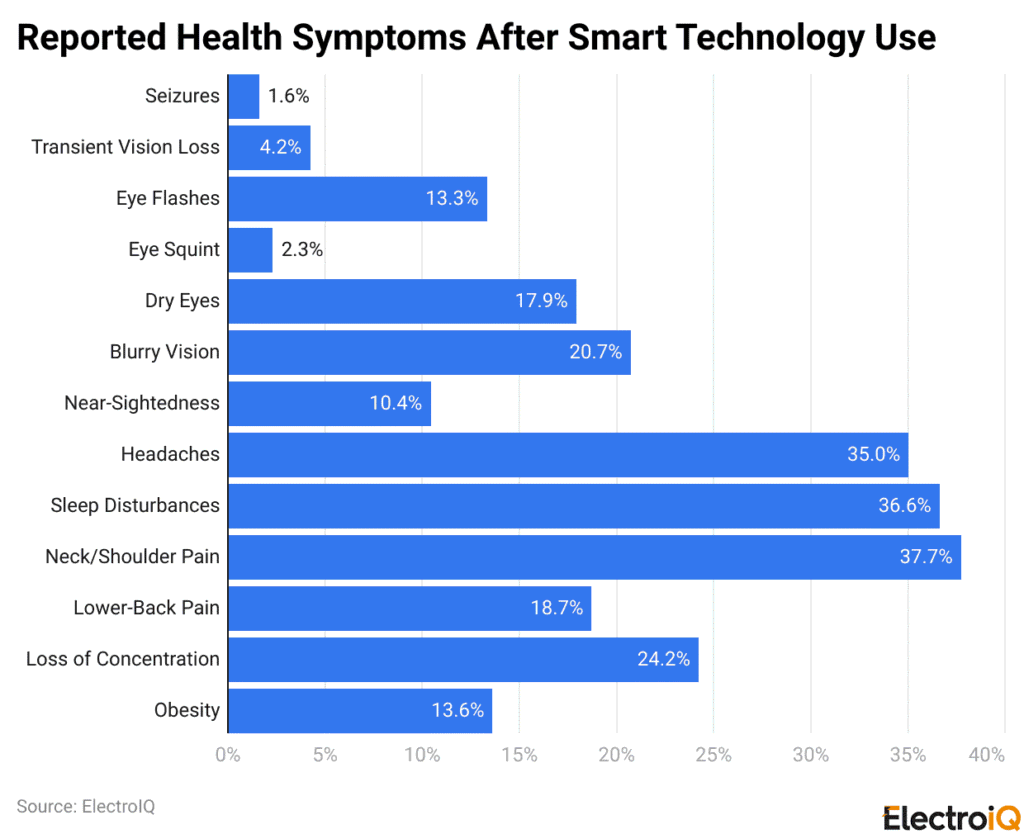
- The reported health symptoms after smart technology use show that neck/shoulder pain (37.70%) is the most prevalent issue, followed closely by sleep disturbances (36.60%) and headaches (35%).
- Screen habits affect sleep, as 85% of Americans use screens within one hour before bedtime.
- A 2025 APA study shows that heavy digital use is linked to a 40% higher risk of depression.
- This year, early exposure to devices can lead to 40% of children owning a tablet by age 2 and 25% owning a cellphone by age 8, according to Common Sense Media.
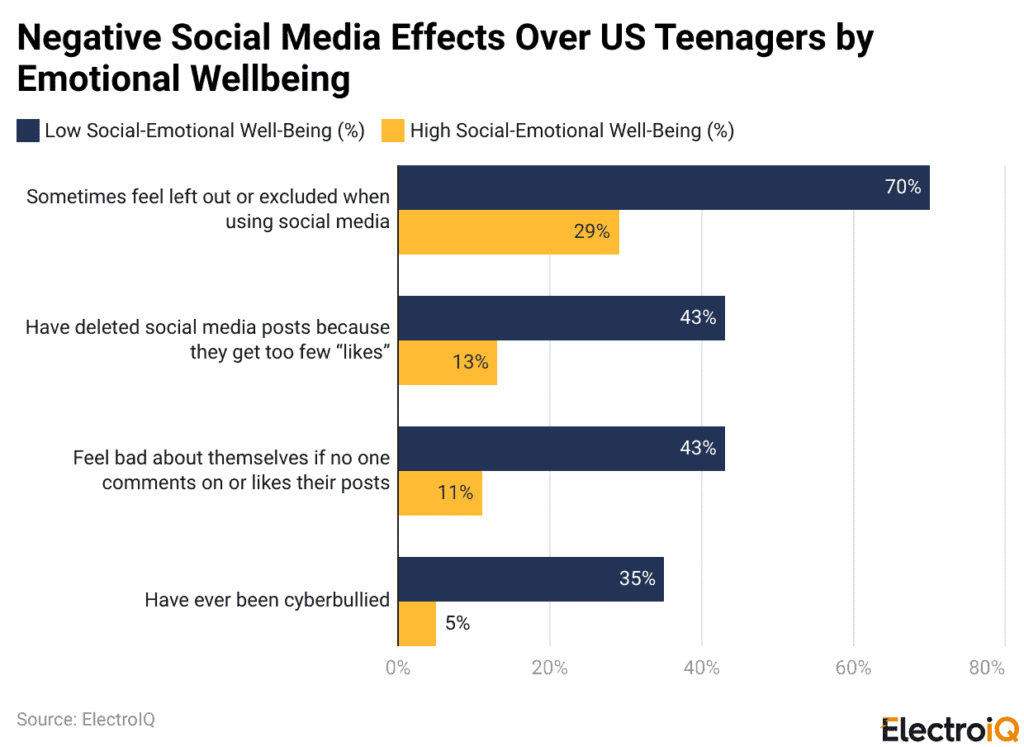
- Social media affects U.S. teens differently, as 70% with low emotional well-being feel excluded, while only 29% of teens with high well-being report similar feelings.
- According to Education Week, more than half of teachers (56%) reported that laptops and tablets distract students.
- A 2025 workplace vision report found that 68% of employees experience digital eye strain, such as dry or blurred eyes, and 59% report reduced productivity as a result.
Digital Technology Affects Statistics In Personal Lives
(Source: tidio.com)
- As of 2025, the greatest negative impact is observed in communication, with 52% of participants reporting noticeable changes.
- Meanwhile, 42% of individuals experience changes in privacy perceptions.
- Followed by our culture (41%), the working process (41%) and the learning process (40%).
Negative Impacts Of Technology Addiction
- A report published by Virtual Addiction further stated that people with internet addiction are 2.2 times more likely to suffer from sleep issues than non-addicted users.
- 68% of young adults who are addicted to smartphones claimed poor sleep, compared to 57% without addiction.
- Around 30% of phone-addicted users eat more fast food and exercise less.
- Sleep loss affects daily life, with over 1 in 3 people experiencing daytime tiredness due to late-night phone use.
- Mental health risks are serious, since over 30% of smartphone-addicted individuals show depression symptoms.
- Teenagers using phones for more than 4 hours daily are much more likely to have suicidal thoughts.
- Additionally, 1 in 3 people believe social media harms their mental health overall.
- Loneliness is also higher, as people who watched online porn in the last 24 hours are nearly twice as likely to feel lonely.
Negative Effects Of Technology Statistics By Workplace Productivity
- According to SQ Magazine, constant digital distractions such as emails, notifications, and chat apps cost the U.S. economy approximately USD 650 billion annually.
- Modern workplaces lose valuable time due to digital overload. Employees now spend 28% of their workweek on emails and another 20% switching between tools.
- As of 2025, productivity will decline by up to 40% due to personal devices and frequent interruptions.
- Approximately 45% of workers report that digital tools slow their work, resulting in a loss of about 51 minutes per week.
- In addition, late meetings after 8 p.m. increased by 16%, with many workers managing more than 50 messages outside normal hours.
- Additionally, TechRadar found that 63% of workers say workplace technology harmed their lives last year, while 41% experienced stress from notification overload.
By Health Symptoms
(Reference: sqmagazine.co.uk)
- The reported health symptoms after smart technology use show that neck/shoulder pain (37.70%) is the most prevalent issue, followed closely by sleep disturbances (36.60%) and headaches (35%).
- Meanwhile, other symptoms include loss of concentration (24.20%), blurred vision (20.70%), lower back pain (18.70%), dry eyes (17.90%), obesity (13.60%), eye flashes (13.30%), near-sightedness (10.40%), transient vision loss (4.20%), eye squint (2.30%), and seizures (1.60%).
By Sleep Disruption Analyses
- Screen habits affect sleep, as 85% of Americans use screens within one hour before bedtime.
- Research shows that blue light can delay melatonin release by 60%, making it harder to fall asleep.
- Young children aged 5 to 10 years who use tablets at night sleep 22 minutes less on average.
- Problems linked to technology-related sleep disorders increased by 19% between 2023 and 2025.
- Research shows that 37% of adults experience disrupted deep sleep due to phone notifications.
- Teens who use screens for more than 4 hours per day are 70% more likely to have poor sleep quality.
- In 2025, about 58% of high school students face chronic sleep loss.
- Sleep-tracking devices also interfere, as 1 in 6 users are awakened by alerts and 40% feel anxious.
- Meanwhile, insomnia in adults aged 30-50 has risen by 12%, largely linked to increased nighttime screen use.
By Mental Health Impacts
- A report share by SQ Magazine, more Gen Z users report social media harming mental health, rising to 56% from 47% in 2023.
- A 2025 APA study shows that heavy digital use is linked to a 40% higher risk of depression.
- Adults who spend over 7 hours a day on screens are twice as likely to suffer from anxiety disorders.
- In the United States, reports show that suicidal thoughts among teenagers rose by 13% from 2023 to 2025.
- Since 2020, the need for teletherapy has climbed by 61%, often linked to excessive technology use.
- People who spend over 90 minutes a day doomscrolling experience 35% lower life satisfaction.
- Only 1 in 4 college students reports feeling lonely online.
- Digital detox retreat bookings increased by 34% in 2024.
- According to a study by Tidio, the top five negative effects of technology are psychological issues (50%), sleep problems (48%), social issues (45%), difficulty forming relationships in the real world (42%) and difficulty with focus (41%).
The Negative Effects Of Technology On Children
- In 2025, early exposure to devices can lead to 40% of children owning a tablet by age 2 and 25% owning a cellphone by age 8, according to Common Sense Media.
- Health agencies like the CDC report that heavy screen use is strongly linked to increased anxiety, depression, and poor mental health among children and teens.
- Data from the American College of Paediatricians indicate that children aged 8-12 spend nearly 5 hours per day on screens, whereas adolescents spend an average of 7.5 hours per day.
- Academic research published by JAMA Network indicates that excessive screen time is associated with lower reading and math performance.
- Medical experts at the Mayo Clinic warn of risks such as obesity, sleep disruption, and attention difficulties.
- At the same time, a Times of India study reports 39.6% of preschoolers suffer sleep problems due to screen exposure.
Negative Social Media Effects On Teenagers’ Emotional Well-Being
(Reference: truelist.co)
- Social media affects U.S. teens differently, as 70% with low emotional well-being feel excluded, while only 29% of teens with high well-being report similar feelings.
- Online validation matters greatly: 43% of low well-being teens delete posts, compared with 13% of high well-being teens.
- When posts receive no likes, 43% of low-well-being teens feel bad, compared with 11% of high-well-being teens.
- Cyberbullying affects 35% of low well-being teens, compared with only 5% of high well-being teens.
Cybersecurity Risks, Scams, and Data Privacy
- According to Cybersecurity Ventures, Global cybercrime is officially projected to cost the world an astonishing $10.8 trillion by the end of 2026, making it an economic force larger than the gross domestic product of most nations.
- According to Constella Intelligence, the total volume of leaked identity records has surged by 135% recently, with 68.89% of all breached passwords now arriving in plain text, making them easier for attackers to weaponise.
- The public and education sectors experienced a massive 569% increase in identity breach volume over the past year, driven by the volume of personal data they hold.
- Across global digital platforms, 4.18% of all identity verification attempts are currently fraudulent, and outright impersonation scams account for more than 85% of those attempts, according to Veriff.
- According to BIIA, Synthetic identity fraud now accounts for up to 80% of all new account fraud cases, inflicting global corporate losses of $20 billion to $40 billion annually.
- A staggering 4.8 million independent phishing attacks were documented globally in a single year, representing a 20% direct increase and marking an all-time high for digital deception.
- Financial services and software-as-a-service platforms bear the brunt of these email scams, accounting for 60% of all recorded phishing volume.
- Malicious attacks using QR codes, known as quishing, have independently surged by 400% since 2023 because these images easily bypass standard corporate email security filters.
- IBM Security Data via Secureframe states that Organizations victimized by a successful phishing breach now face an average financial cost of $4.8 million per isolated incident
- AI-generated phishing emails achieve a dangerously high 54% click-through rate, which drastically overshadows the 12% success rate historically seen with traditional human-written scam messages
Negative Effects Of Technology On Education
- According to Education Week, more than half of teachers (56%) reported that laptops and tablets distract students.
- One-third reported that learners remain off-task for more than 25% of class time.
- Data from IES (ies.ed.gov) indicate that 53% of school leaders report that cell phones are linked to lower academic performance.
- Meanwhile, 73% noted poor attention, and 72% raised mental health concerns.
- A 2025 JAMA Network study found that each additional hour of screen time reduces the odds of reading and math achievement by 9%-10%.
- Research published in SpringerLink links 66.67% of digital distractions to poor personal performance and 23.33% to classroom disruption.
- A Guardian survey of 2,000 teens stated that 62% felt AI harms learning, and 25% claimed it made the work process easier.
- Meanwhile, compareandrecycle.co.uk reports 65% of parents worry about physical development and 69% about mental health effects.
On Employees
- A 2025 workplace vision report found that 68% of employees experience digital eye strain, such as dry or blurred eyes, and 59% report reduced productivity as a result.
- The Forbes report further states that digital overload also affects efficiency: 45% of workers report that technology tools slow their work, resulting in 51 minutes per week, or about 44 hours per year, lost to tool fatigue.
- Additionally, 56% of workers report that constant app switching and alerts harm performance in 2025.
- Monitoring technology adds stress, since 96% of companies use time-tracking tools, 70% of large firms monitor staff, yet 72% of employees believe monitoring does not improve results.
- Overall, workplace technology in 2025 is linked to lower productivity, higher stress, and declining employee well-being.
The Impact of AI on Job Security and Anxiety
- According to Astrotalk, Career-related anxiety rose by 50% in 2025 compared to the previous year, with “Is AI going to take my job?” becoming the most frequent professional inquiry among users seeking guidance.
- According to the Pew Research Centre, approximately 52% of U.S. workers report being worried about the future impact of AI in their workplaces, while 32% believe the technology will lead to fewer long-term job opportunities for them.
- Exploding Topics Research Says that High-income earners—specifically those with household incomes over $200,000—report the highest levels of anxiety, with nearly 73% using AI more frequently than a year ago but feeling the most at risk of replacement.
- Nearly 1 in 20 layoffs in 2025 (4.5%) were officially attributed to AI-related restructuring, contributing to a sense of “organisational betrayal” among long-term employees, according to Oxford University / PMC Study in 2025.
- edX Research states that Millennials are the most stressed generation regarding job security, with 54% viewing AI as a direct threat to their roles and 67% feeling forced to upskill or reskill to remain employable.
- Psychological evaluations of displaced workers found that 100% of study participants experienced acute emotional volatility, including shock, insomnia, and a “shattered sense of self,” particularly when roles were eliminated shortly after receiving high-performance awards.
- Only 4% of employees are currently pursuing AI education despite 84% acknowledging that AI skills are essential for career survival, creating a “readiness gap” that fuels chronic stress.
- According to Microsoft Work Trend Index, Roughly 33% of workers report feeling “overwhelmed” by the pace of tech-driven change, with 1 in 3 stating that the increasing speed of work over the last five years has made it impossible to keep up.
- The transition to AI-driven environments has led to a measurable increase in “technostress,” a condition where the loss of human agency and constant digital monitoring are significantly associated with emotional exhaustion and depressive symptoms.
- According to McKinsey, Global estimates suggest that 14% of the workforce, or 375 million people, will be forced to change their entire career paths by 2030 due to automation, leading to a “psychological crisis” for mid-career professionals.
The Environmental Impact of Technology (E-Waste)
- According to Upcycle That, Global electronic waste generation has reached over 53 million metric tons annually, and current data indicates this digital waste is increasing by 2.6 million tons each year, potentially reaching 82 million tons by 2030.
- TTMS reports that the electricity consumption of artificial intelligence and global data centres reached approximately 415 terawatt-hours in 2024, representing about 1.5% of total worldwide electricity use.
- Forecasts estimate that data centres will consume over 500 terawatt-hours by 2026, pushing their share to 2% of all global electricity consumption as artificial intelligence infrastructure expands.
- According to Food and Water Watch, Artificial intelligence text searches on platforms like ChatGPT consume nearly 10 times as much electricity as a standard Google search, significantly driving up daily energy demand.
- As per MIT News, meeting the rising energy demands for global data centres will require burning more fossil fuels, which is projected to increase global carbon emissions by about 220 million tons.
- Climate Impact Partners stated that training a single large artificial intelligence model, such as GPT-3, emitted roughly 500 metric tons of carbon dioxide, which is equivalent to the emissions from driving a car from New York to San Francisco about 438 times.
- Only about 17.4% to 20% of global electronic waste is formally collected and properly recycled each year, leaving the vast majority of dangerous devices dumped in landfills by The Cool Down.
- Europe leads the world in formal collection with a 42.8% recycling rate, successfully recycling about 7.5 kilograms of the 17.6 kilograms of electronic waste generated per European citizen on average.
- According to Tier1 News Team, over $57 billion worth of precious metals like platinum, gold, and copper are lost each year globally because discarded electronic devices are not safely recycled back into the supply chain.
- During the formal electronic waste recycling process alone, about 1 billion kilograms of valuable metals are permanently lost, even though 6 billion kilograms are successfully recovered.
Conclusion
After reviewing the article as a whole, it can be suggested that technology can pose serious challenges and negative impacts on our daily lives. Nowadays, in many areas, more than six hours per day is spent on screens, and excessive screen use is often associated with poor sleep and higher stress. Social media also includes many harmful sides of technology that contribute to increasing loneliness, stress and sadness, particularly among adolescents.
Many teens face cyberbullying every year. At the workplace, frequent online notifications disrupt concentration and can lead to many errors. Meanwhile, increasing data breaches increase the risk of scams and identity theft.

