Introduction
Cybercrime Statistics: The year 2025 witnessed that illicit digital activities no longer remained an intangible issue but were presented as a line item in financial statements. These had appeared in the budgets of companies and households. The online crime, laptop, and economic impact have reached a new level. It is even speculated that the latter has overshadowed the former.
In this article, the author assembles the most trustworthy, research-based numbers for 2025 and clarifies their implications in terms of dollars and percentages. Furthermore, it brings to light the specific areas that organizations and individuals should target to weaken the coming storm of attacks.
Editor’s Choice
- The FBI’s report of the cybercrime losses was US$12.5 billion in 2023, with 880,000+ complaints filed, but actual worldwide losses may be many times higher.
- The total cost of cyber crimes to the world was US$1.2 trillion in 2019, and the figure is estimated to have climbed to US$7.1 trillion in 2022 due to higher digital usage and a series of crypto-related hacks.
- Ransomware is now a common malware, with its share of incidents being about 27%, and most organizations expect at least one ransomware attack per year.
- Fraud on social media is a very common practice, with LinkedIn being responsible for almost half of the social media phishing attempts, and one-fourth of the victims coming across fraud via social networking.
- Data leaks are becoming more prevalent and larger in size, with the detection and containment sometimes taking months, which in turn raises the overall expense considerably.
- Cloud security breaches are quite common, as 61% of companies suffer at least one cloud attack per year, usually resulting from poor configuration and employee mistakes.
- Among the other significant factors that have led to losses are tech support scams, personal data leaks, romance scams, and impersonation of government officials, the last one being the case of AI-enabled impersonation that’s responsible for a 64% increase in such fraud yearly.
- The healthcare sector has been the most affected financially, losing almost US$9.8 million on an average breach, and having hundreds of ransomware attacks in the case of a single year.
- Phishing is now the most frequent type of cyberattack, accounting for more than 50% of all online criminal activities, and replacing non-payment and non-delivery scams that were the most common in 2017.
- The elderly population is the most affected group, where people aged 60 and above lost almost US$4.8 billion in one year.
- The upsurge in cybercrime for 2024 reached a staggering US$16.6 billion, which is 33% more than the previous year, though the number of reported complaints has slightly decreased.
- AI is like a two-sided sword; on the one hand, it makes the scams more convincing, and on the other, it helps organizations to come up with faster and better strategies to detect and respond to breaches.
- The anticipated global cost of cybercrime is US$9.22 trillion in 2024, and it will soar up to US$13.82 trillion by the end of 2028 as the attacks will keep on becoming more massive and sophisticated.
- The increasing trend in cybersecurity spending is very rapid, and the global investment is about to reach US$184 billion, along with an enormous rise in AI-driven and zero-trust security solutions.
- Investment fraud is the most expensive type of cybercrime, which is responsible for nearly 37% of the total reported losses, and another major area is business email compromise, which costs about US$3 billion.
The Costliest Type of Cybercrimes
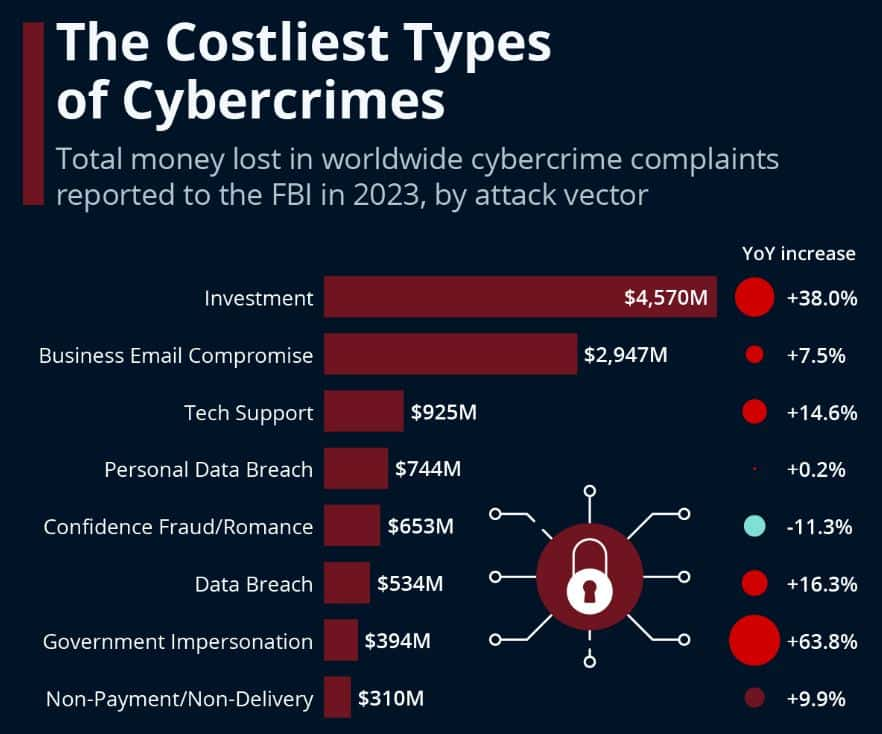
(Source: statista.com)
- In 2023, cybercrime-related losses reported to the FBI reached US$12.5 billion worldwide, surpassing the US$10 billion threshold for the second consecutive year.
- According to a report released in April 2024, this figure likely underrepresents the true scale of cybercrime, as it only includes incidents reported through the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), with the majority of submissions coming from the United States.
- More than 880,000 complaints were recorded, with financial losses largely concentrated in two primary attack methods.
- Data compiled by Statista using FBI figures shows that investment fraud accounted for about 37% of total reported losses.
- This category includes schemes such as Ponzi operations, pyramid scams, and deceptive retirement investments that promise high returns with little risk.
- Business email compromise was another major contributor, resulting in approximately US$3 billion in losses through phishing and social engineering attacks that allowed criminals to access corporate accounts and initiate fraudulent transactions.
- Additional fraud types responsible for substantial losses include tech support scams, which caused US$925 million in damages, personal data breaches totalling US$744 million, and romance scams leading to losses of US$653 million.
- Alongside investment fraud, government impersonation scams experienced the largest year-over-year increase, with stolen funds rising 64% compared to 2022.
- This surge may be connected to the growing availability of AI tools, such as ChatGPT, which can be misused to convincingly impersonate public figures.
- A notable example reported by the Associated Press in February 2024 involved a political consultant paying US$150 to generate an AI-based voice impersonation of U.S. President Joe Biden to discourage voter participation.
Share of Worldwide Types of Cybercrime
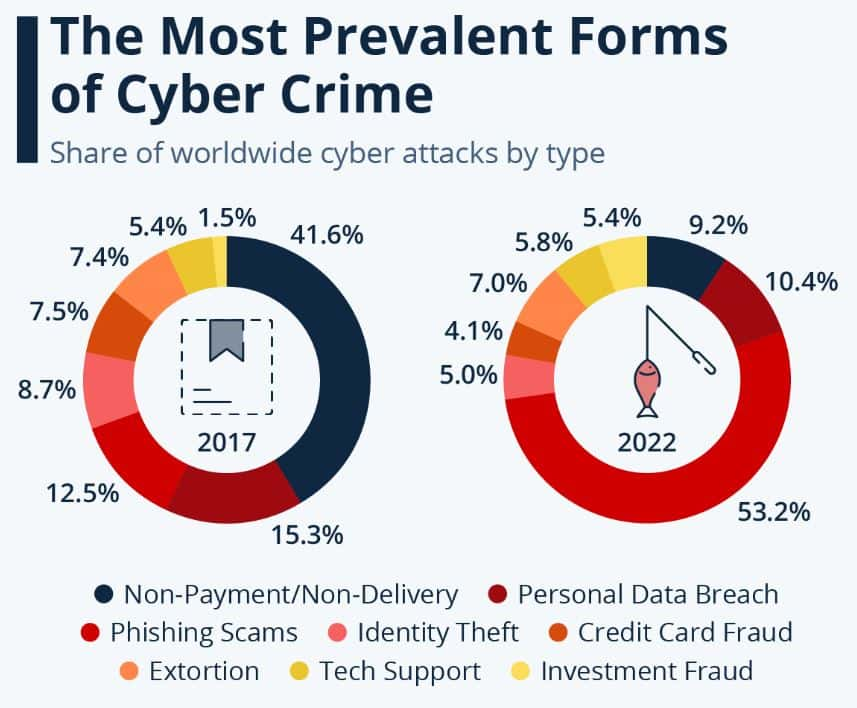
(Source: statista.com)
- The FBI presented global cybercrime losses of around US$12.5 billion in 2023, showing that those attacks have become a highly profitable avenue for criminals.
- The pandemic, which caused the entire world to switch to online activities, is one of the factors that have contributed to the rise.
- The digital attack surface was thus expanded. In terms of Statista, global cybercrime losses reached an astounding US$7.1 trillion in 2022, which is a huge leap from US$1.2 trillion in 2019.
- Cryptocurrency courts and exchanges have witnessed a lot of breaches, with some security experts likening these to state-backed groups, specifically North Korea’s Lazarus Group, and this has been particularly intense during 2021 and 2022, as per Chainalysis reports.
- Even though the number and the impact of cyber attacks have been on a steady increase, the attacks have changed character massively over the last five years.
- In 2017, approximately 42% of non-payment or non-delivery scams, like counterfeit online purchases or payments that never got to the right person, were the main reported cybercrimes.
- Furthermore, personal data theft and phishing attacks were responsible for another 28%, while identity theft, credit card fraud, and other types of cybercrime shared a smaller amount.
- However, phishing is now the most common type of cyber attack. In the last year, over 50% of all online criminal activity was associated with phishing.
- Attackers have constantly tailored their techniques according to the channel and the target, despite email-based phishing being one of the earliest types of fraud on the internet.
- Among these are spear phishing, which targets specific people or teams in the organization, whaling targeting high execs in the company, as well as smishing through texts and vishing via calls.
Expected Annual Cost of Cybercrime
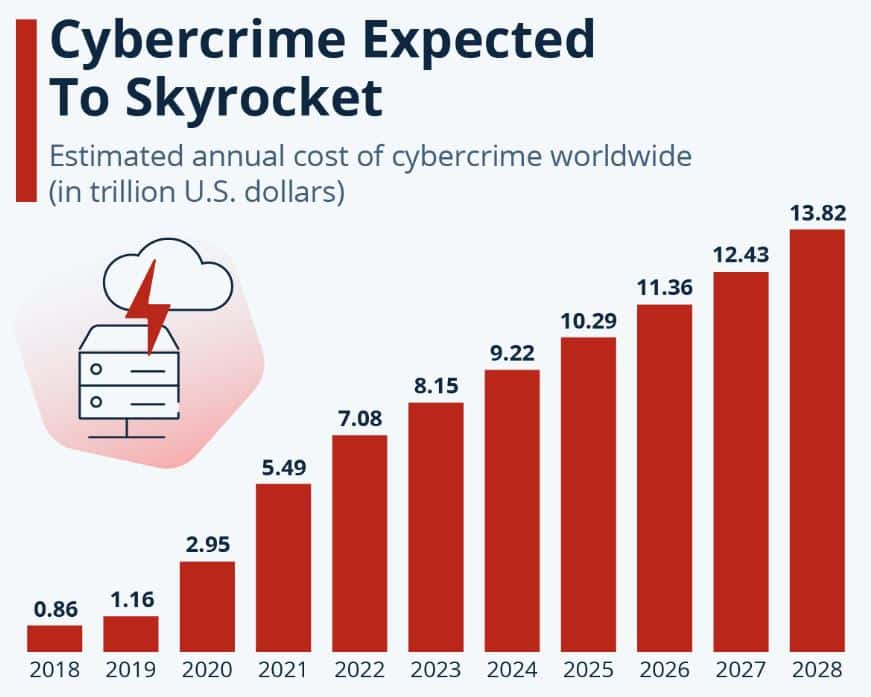
(Source: statista.com)
- Statista’s Market Insights forecasts that the financial impact of cybercrime on a global scale will keep increasing through the years to come, starting with the estimate of US$9.22 trillion in 2024 and culminating with the even higher figure of US$13.82 trillion by 2028.
- The massive growth of the internet in every aspect of human life – work and leisure – has opened up a vast number of people who could be targeted by cybercriminals.
- In addition, the attack techniques have become more intricate, going hand in hand with the availability of various tools that make the scams and intrusions happen.
- One could say that the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic was a critical point in this development. Statista’s Market Insights analysts commented that the universal shift to telecommuting and the sped-up transition to virtualized IT.
- Especially, cloud-based infrastructures, data, and networks have all been factors that made the cyber threats stronger since they come with new security gaps.
Complaints And Losses To Cybercrime Statistics
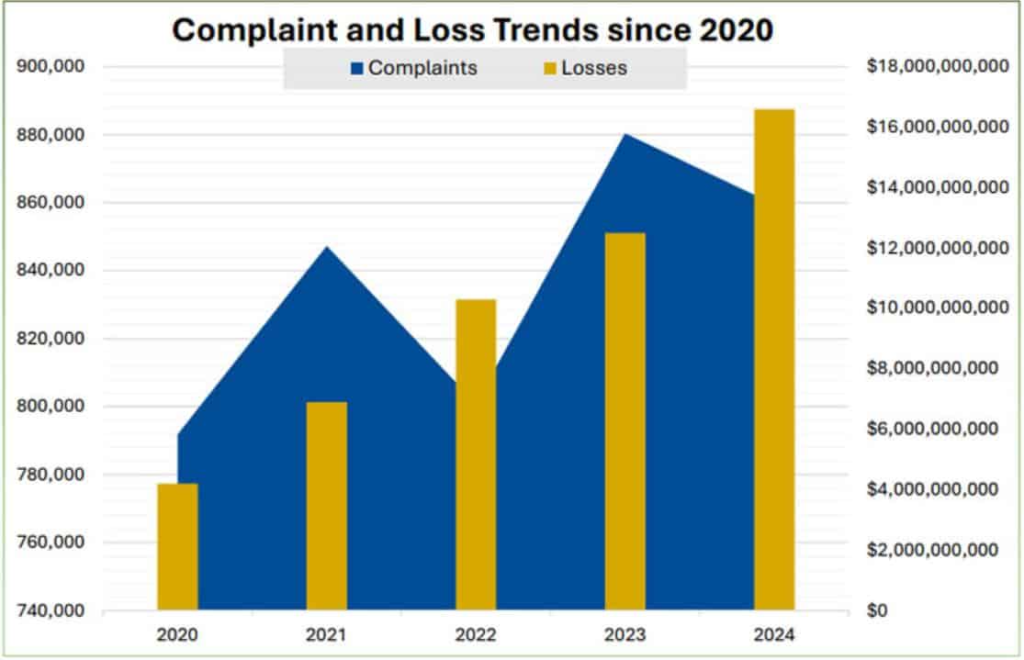
(Source: hipaajournal.com)
- The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) disclosed its 2024 Internet Crime Complaint Report, stating that the losses due to cybercrime had reached an unprecedented height in 2024.
- On the other hand, the total number of complaints did not change much from the previous year, but the amount of money lost increased significantly by 33% to US$16.6 billion, exceeding the US$15.4 billion loss that was reported in 2023.
- Cyber-enabled fraud accounted for 83% of all the losses and also for 38% of all the complaints.
- The IC3 received 859,532 complaints in total, out of which 256,256 cases involved actual financial loss. Each victim lost an average of US$19,372 in an incident.
- Phishing and spoofing were again the top-reported crimes, with above 193,000 complaints being filed. Among the other frequent problems were extortion and breach of personal data.
- As far as money lost is concerned, investment scams were the biggest loss-makers, with a total of US$6.57 billion.
- Business Email Compromise came second with US$2.77 billion in corresponding losses.
- Tech support scams and personal data breaches were also significant, contributing US$1.46 billion and US$4.45 billion, respectively, to the total losses.
- Victims aged 60 and older were the most affected, suffering a loss of nearly US$4.8 billion.
- Ransomware incidents also saw a steep rise in numbers in 2024, with complaints climbing by almost 12%.
- These attacks turned out to be particularly damaging to the critical infrastructure, with the healthcare sector being one of the most affected, as it alone reported hundreds of ransomware attacks and data breaches throughout the year.
Cost Of Data Breach By Region
(Source: verimatrix.com)
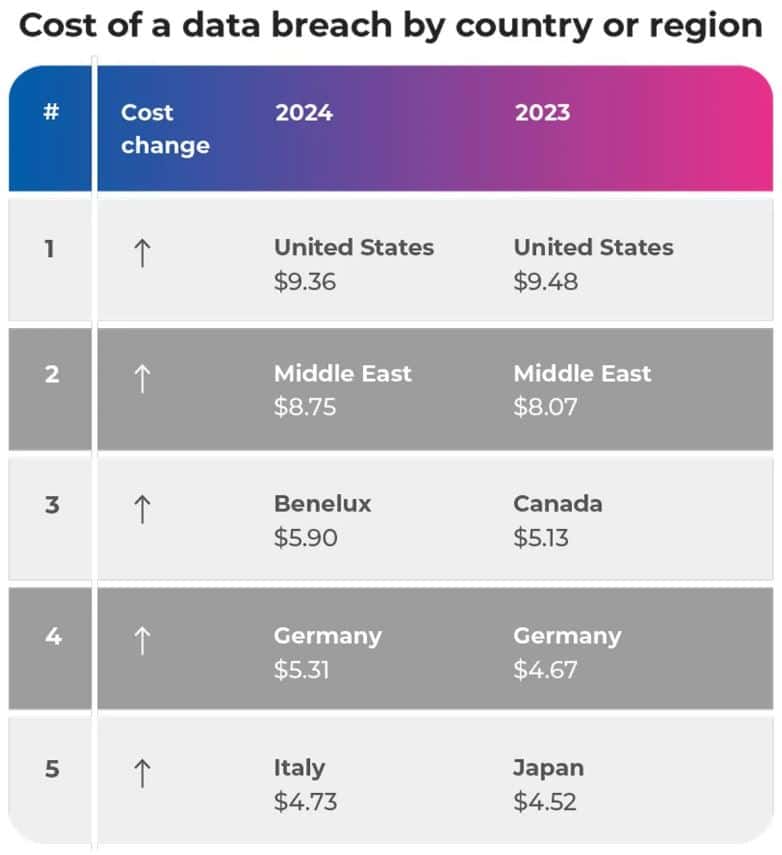
- A continual trend for the United States is the recording of the highest average cost of a data breach, which is taking place for the 14th year straight.
- The average cost in the United States in 2024 was reported to be US$9.36 million. It is slightly lower than the 2023 amount by US$0.12 million, but remains significantly higher than the other regions that have participated in the study.
- The Middle East, which is the second-highest after the U.S., reported an average breach cost of US$8.75 million, which was an increase from the previous year at US$8.07 million.
- For the first time, Benelux appeared in the top rankings with the average cost of US$5.90 million.
- Germany, too, experienced a rise in average breach costs from US$4.67 million to US$5.31 million, while Italy recorded a substantial increase from US$3.86 million to US$4.73 million.
- On the other hand, some regions got better. In Canada, the average cost of data breaches was down from US$5.13 million to US$4.66 million, and in Japan was also down from US$4.52 million to US$4.19 million.
- The differences portray that regions are quite different when it comes to their cybersecurity preparedness, regulatory pressures, and susceptibility to changing cyber threats, all of which have a strong effect on the financial impact of data breaches.
Social Media Scams And Phishing Threats
- The social media websites are now the prime place for online scams and cybercrime, which is mainly due to their enormous number of users and the fact that people have a high level of trust in messages they receive through these networks.
- Phishing accounts for about 8% of all cyber-attacks related to social media, where the attackers deceive users into giving away their sensitive information or clicking on harmful links.
- LinkedIn has become the major platform targeted by hackers, which is responsible for 47% of all phishing attempts done through social media.
- The primary reason for this is its professional-oriented nature, where the probability that users will trust messages about jobs, business opportunities, or networking is highest.
- The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) claims that social media has turned into a “golden goose” for con artists, with one out of four victims stating that the fraud started with a contact through social media.
- Fraudsters mainly take over genuine accounts on various platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and LinkedIn, and later on, they use these accounts for sending phishing messages to users who are not aware of the scam.
- Facebook has also experienced large-scale data leaks in the past, which have been a contributing factor to the over-generalized issue of data exposure.
- In addition to social media, hacked accounts are frequently sold at a very low price on the dark web. For instance, over 50,000 Zoom account passwords have been exchanged for a few cents each.
- On the whole, mobile applications are responsible for about 70% of online fraud cases now, which illustrates the escalating risk associated with social and mobile platforms.
Ransomware Attack Growth
- The statistics reveal that ransomware has turned out to be one of the most prevalent and expensive forms of cybercrime.
- At present, approximately 27% of all malware attacks are ransomware-related, indicating the high frequency at which this menace is exploited by attackers.
- For ransomware, medium and small enterprises face the worst impact, as the cost share of such attacks is approximately 51% of their overall cyberattack-related expenses, and this trend is likely to continue as attacks become more technologically advanced.
- Financial services record a 9% rise in the number of ransomware incidents, while the entire industry reports an increase of over 100% per year in ransomware attacks.
- Speculations indicate that 76% of organizations will face a minimum of one ransomware attack each year, thus treating it as a common and recurring risk instead of an episodic one.
- More and more attackers are disabling the recovery options as their primary targets.
- Backup systems and repositories are directly targeted in 96% of ransomware attacks, so that organizations have no choice but to pay the ransom if they want data restoration.
- The majority of attacks are rapid once access is obtained, with 77% of incidents witnessing ransomware use within 30 days of the first interaction and over half within just seven days.
- The average time from the first access until ransomware release is around 6.1 days.
- The show of power in high-profile cases like the Transport for London attack compromised sensitive customer data. The health care sector is still financially the most impacted area, with an average breach cost of US$9.8 million and more than 630 ransomware incidents in a single year.
Device And Cloud Security Threats
- The percentage of organizations facing cloud-related security issues is on the rise, with up to 61% of businesses reporting at least one cloud attack every year.
- About 21% of these cloud-related incidents escalate into confirmed data breaches.
- Security problems surrounding the public cloud affect approximately 27% of the business operators, with almost a quarter of that number directly arising from incorrect configurations.
- The human aspect continues to be a major vulnerability, with humans being the cause of over half of all cloud breaches.
- The number of internet-enabled devices continues to grow, and the risks associated with them are significant, as it is estimated that attackers can access up to 70% of the IoT devices.
- The medical sector, especially the NHS, has recognized that almost 46% of its IoT devices have to deal with at least one known security vulnerability that has not been fixed.
- Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks are progressively becoming more common, with an annual increment of approximately 20%. Even though the authorities managed to shut down 48 DDoS-for-hire services in just one year, new sites are being established with the same speed.
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities And Breaches
- Cyber threats have gone up in sophistication, and many organizations have not improved their preparedness, resulting in drastic financial and operational effects.
- A study has pointed out a growing paradox concerning artificial intelligence: AI is a double-edged sword, as it not only fortifies the defences but at the same time, creates new attack surfaces.
- More than 50% of business leaders acknowledge that AI is a source of risk, especially through generative AI phishing, voice deepfakes, prompt manipulation, and synthetic media.
- At the same time, numerous firms are treating AI as a friend rather than a foe by employing it for detection automation, advanced threat hunting, and workforce upskilling, training employees on the AI-related risks, and being the majority in the process.
- Security loopholes are still increasing very fast, as new CVEs numbering in the hundreds are being found every quarter, and critical flaws are having a yearly rise.
- Prominent systems and frameworks such as Linux, Android, Log4j, and MoveIt have become the main targets, which is putting the security of hundreds of millions of records at risk.
- There is an upward trend in the frequency and size of data breaches, and it is common for it to take several months to discover and contain them.
- The cost savings that come with quicker detection of breaches, especially for those who use AI, are significant; however, the healthcare and entertainment sectors are still the ones that suffer the longest in terms of time taken to respond.
Cybersecurity Statistics By Industry
(Source: vikingcloud.com)
Survey data for a future year may be a little less accurate, but still useful for a general idea. The industry-specific cyber threats are still present, particularly in the healthcare sector, financial sector, insurance, and government. All, at least, are projected to have the same operational cost increase.
Healthcare
- Healthcare is one of the industries that hackers target the most, and it is the one where the cyberattacks are mostly concentrated among different sectors.
- Ransomware is the number one cause of such attacks, and the plus side is that the growth rate of the attacks at health care providers, hospitals, and clinics is 25% or more.
- A staggering 68% of healthcare executives stated that they were being attacked at least twice a year on average, which shows how normalized such breaches have turned out to be in the healthcare industry.
- This alarming statistic led to more than 70% of hospitals in the United States that participated in a survey conducted by the Department of Health and Human Services endorsing the NIST cybersecurity frameworks as the means to reinforce their protection.
- While the yearly expenses incurred on healthcare data breaches are falling at the rate of approximately 10.6% per year, the situation overall is still worrisome.
- The total costs from healthcare breaches have increased by 53% since the onset of the pandemic.
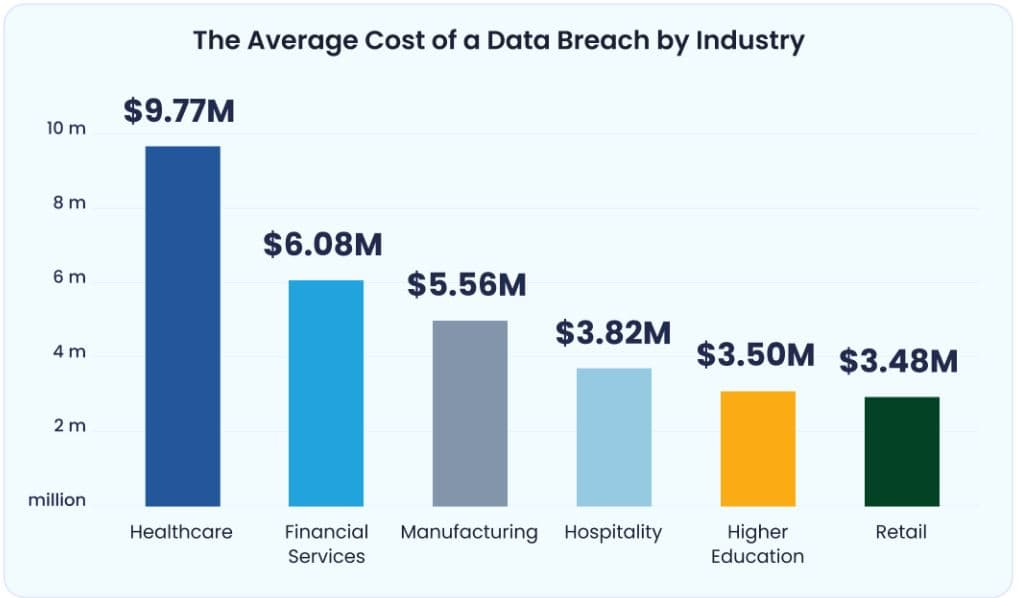
- The average cost of an incident in the healthcare sector reached US$9.77 million in 2024, thus marking it as one of the most costly sectors in terms of cyber incidents.
Finance And Insurance
- Cybersecurity has become a never-ending battle for banks and insurance companies.
- Accordingly, attacks against APIs and web apps rose by 65% over the previous year, whereas phishing alone ensured that the financial sector ranks among the top three most attacked industries.
- The number of malicious bots has also skyrocketed, and in some instances, requests made by bots increased by as much as 69% compared to the previous year.
Financial Sector Manufacturing Hospitality
These threats come with very large financial implications. The costs related to data breaches in the finance industry went up by about 2.3% yearly, and the average enterprise was almost US$5.9 million worse off per breach. Briefly, the total costs for breaches in financial services are generally between US$5.86 million and US$6.08 million. This indicates the high worth of financial data as well as the consequences of exposing it through regulatory fines.
Manufacturing
- Ransomware has made the role of manufacturing the main target due to the fact that the sector uses a lot of operational technology and needs continuous uptime.
- 44% of the computers that are used in manufacturing settings get infected with ransomware every year on average, and about 62% of the companies that have been affected decide to pay the ransom.
- The cost of a manufacturing data breach has been estimated to be US$5.56 million in 2024.
- In addition, attackers frequently use stealthy methods where they gain access through a backdoor, which contributes to 28% of the malicious actions in the sector.
- Usually, these attacks remain undetected for a long time; thus, the firm suffers for a longer time and also incurs higher recovery costs due to extended disruptions.
Hospitality
- The hospitality sector experiences a higher risk of cyber attacks during the famous travel periods.
- It was reported in North America that 90% of hotel IT and cybersecurity managers encountered at least one cyberattack during the summer of 2024.
- Out of the total respondents, 82% stated that there was at least one successful attack, and almost half of the respondents admitted that their systems were down for over 12 hours.
- On the other hand, over half of the hotel security leaders mentioned five attacks or more during the peak season, while two-thirds reported that the frequency of attacks had increased, and half stated that the attacks were more severe.
- Deep-learning technology is also making an impact on the threats, as almost half of the hospitality security executives mentioned that it was hard for the personnel to detect deepfakes and similar attacks.
- Increased credit card usage during busy travel periods also raises risk, according to 32% of hotel IT leaders.
- Hotels working with managed security service providers showed stronger resilience, with 80% resolving incidents within 12 hours.
Education Sector
- Educational institutions, particularly K–12 and higher education, have seen a sharp rise in cyberattacks.
- Attacks on K–12 schools surged by 92%, while educational organizations experienced a 70% increase in attacks overall within a single year.
- The U.S. accounted for 80% of known ransomware incidents during this period.
- Ransomware actors aggressively target backups, with 95% attempting to access data recovery systems.
- Nearly all higher education institutions reporting ransomware incidents experienced significant revenue losses.
- Each day of downtime can cost schools up to US$550,000, and the average data breach cost for higher education stands at US$3.65 million.
- Over five years, ransomware-related downtime has cost the education sector more than US$53 billion.
Retail
- Retailers continue to face widespread cyber risk, particularly from third-party vendors. Nearly 97% of major U.S. retailers experienced third-party data breaches in the past year.
- Security breach costs in retail rose by 18% year-on-year, and the sector accounts for 6% of all global data breaches annually.
- The average retail data breach costs US$3.48 million, but the broader impact extends beyond direct expenses.
- Around 80% of retailers reported at least one successful cyberattack in the past year, with many facing multiple incidents.
- Downtime and operational disruption affected 68% of retailers, while 45% reported supply chain issues and lost sales.
- The cyberattacks, which also triggered a financial storm, caused stock price declines in almost a quarter of the retailers, and one-third of the companies had to pay fines to the government for not complying with data protection regulations.
Security Investment Trends
- In the fight against digital risks, in the first place, organizations all over the world are making a significant upturn in their expenditures for cybersecurity.
- It is foreseen that global expenditure on information security will go up by approximately 15% within the next year; hence, the total annual spending will be close to US$183.9 billion.
- The demand for security services is probably the biggest contributor to this growth, as these services are forecasted to grow even faster than the investments made in traditional software or network security tools.
- On average, cybersecurity budgets are growing by 8% every year; that is, acknowledgement of security as a necessary business function rather than an optional cost has kept the budget increasing accordingly.
- The whole of the cybersecurity market is also experiencing a strong rise and is projected to have a compound annual growth rate of about 7.92% till the end of the decade.
- The increasing adoption of AI and automation is one of the main reasons for this.
- A company that backs out its AI-powered security tools can lower its security budget by US$2.2 million a year on average.
- Organizations that are employing security automation and AI actively save US$1.8 million a year less due to breaches and collect more than US$3 million per data breach as their total assets.
- Thus, the AI cybersecurity market is predicted to reach US$133 billion by 2030.
- The zero-trust security approach is also on the rise. By the end of this year, the value of the identity and access management market is projected to be more than US$24.1 billion.
- As of now, 41% of companies have gone for the zero-trust architecture path, while 83% of the IT staff of small and mid-sized businesses make it mandatory for their employees to use multi-factor authentication.
Cybersecurity Skills Shortage And Workforce Predictions
- Investment increase notwithstanding, the security of cyberspaces still has a shortage of skilled labor as its major problem, with a global deficit of about four million professionals.
- Almost half of the people working in the cybersecurity industry regard a lack of skills as the hardest thing to deal with.
- The number of unfilled cybersecurity jobs in the United States is approximately 570,000, and states like Texas, California, Florida, New York, and Virginia are where the biggest number of vacancies is located.
- Job demand keeps increasing at an amazing rate, though. The U.S. cybersecurity workforce will experience a 33% increase by 2033, equating to about 17,300 new IT security analyst positions every year.
- The information security analyst job market is growing 29% faster than the average of all occupations, thus leaving behind the computer-related roles in general.
- Organizations are heavily investing in technology to fill the gaps created by skilled labor shortages.
- It has been reported that 63% of businesses are looking to adopt tools like Generative AI for managing the shortage, and 41% are already taking advantage of GenAI in this regard.
- In the near future, GenAI is likely to reduce the requirement for specialized training in up to 50% of entry-level cybersecurity positions by 2028, and 40% of C-suite executives would depend on it to combat the shortage of critical skills.
Biggest Data Breach Fines
(Reference: statista.com)
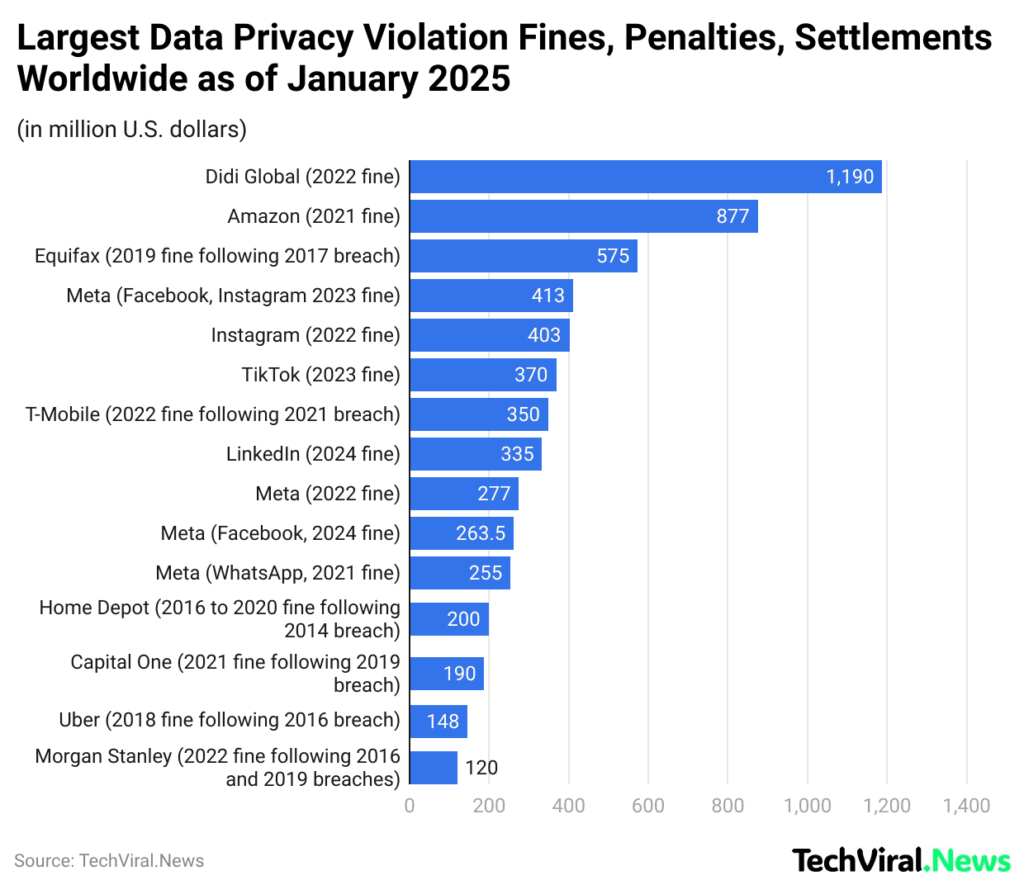
- By the time January 2025 rolled around, the list of the world’s heaviest fines for data privacy violations served as a reminder of the tough stance that regulators now take regarding breaches of personal data. The largest fine ever imposed was meted out to Meta, the parent company of Facebook. The Data Protection Commission of Ireland slapped a record fine of €1.2 billion (approximately US$1.3 billion) on Meta in May 2023 for misusing user data and violating EU data protection laws, thus making a landmark ruling under GDPR.
- The next penalty in line was for Didi Global, a Chinese company trading in ride-hailing and rental cars.
- The data privacy commission of China imposed an 8,026 million yuan fine on Didi in July 2022, which is around US$1.19 billion, for serious violations concerning the handling and protection of customer data.
- This is also a very expensive one since in 2021, the Luxembourg data protection authority fined the company US$877 million for noncompliance with EU privacy regulations, thus constituting one of the largest data privacy penalties ever.
- There was another instance that got our attention, Equifax, which had to pay a fine of US$575 million in 2019, in which the breach of data exposed the private information of almost 150 million people.
- The break-in happened through unpatched security flaws, thus signalling that poor security practices can result in enormous financial and reputational losses.
Conclusion
Cybercrime Statistics: The 2025 cybercrime landscape maps out the scenario. Digital risk has permanently entrenched itself as an escalating economic threat. This is instead of being a temporary technical challenge. All categories contribute to rising losses. These range from phishing and social media fraud to ransomware and large-scale data breaches. Healthcare, finance, and critical infrastructure bear the brunt of the losses.
Even though organizations are trying out many AI, zero-trust frameworks, and automation, the shortage of cyber skills and the ever-expanding attack surface still curtail the defense capabilities. The estimated cost of cybercrime by the end of this decade is over US$3 trillion. Therefore, it is a matter of resilience for the long term. This will depend upon faster detection, advanced technology, workforce development, and strong regulatory enforcement worldwide.
FAQ
Cybercrime is wreaking havoc across economies on a global scale. By 2028, global losses are expected to increase to US$13.82 trillion, rising from an estimated US$9.22 trillion in 2024, according to the scale and sophistication of the attacks. The FBI reported losses amounting to US$16.6 billion in 2024, but experts suggest that this is just a small portion of the actual impact due to global underreporting.
Presently, phishing and investment fraud are the most damaging types of cybercrime. Phishing has become the major contributor to over 50% of the criminal activities on the internet, while investment fraud accounts for nearly 37% of the total reported financial losses alone.
Healthcare is the industry with the highest financial impact, as average breach costs amount to around US$9.8 million for each case, and there are hundreds of ransomware attacks every year. Besides, Finance, Manufacturing, Retail, Education, and Hospitality suffer heavily due to data breaches, ransomware, and operational disruptions, which come in different forms along with their own regulatory issues for each sector.
Ransomware represents around 27% of all malware attacks, and its characteristics include speed, selectivity and destructiveness. Annual coverage of ransomware attacks is assumed to be at least 76% of organizations, and. the remaining 24% get attacked but recover their data because the attackers did not destroy the backup system.
Cybersecurity investment is the way organizations are responding, and total global spending is expected to be around US$184 billion annually. To reduce the cost of breaches and increase the speed of response, a lot of organizations are investing in AI-based security solutions along with automation, zero-trust frameworks, and multi-factor authentication.

