Introduction
Auto Loan Performance and Default Statistics: The year 2025 turns out to be a pivotal year for the auto loan market, heralding an opportunity. Initially, the pandemic led to a sharp decline in prices and a gradual economic recovery, which in turn drove a spike in demand and auto-loan disbursements. However, the subsequent sharp rise in loan amounts, delinquencies, and lender-consumer stress is now the main issue confronting the auto finance industry.
Lower credit tier borrowers are the ones suffering the most. Global vehicle prices have not only reached but also surpassed their previous peaks, to the extent that monthly payments are considered extremely burdensome. It is on this basis that lenders, consumers, and policymakers are all in the same boat when it comes to the year being an issue.
This article intends to help us recognize the trends behind the Auto Loan Performance and Default Statistics, and to give an understanding of what is being indicated for the overall economy by the numbers.
Editor’s Choice
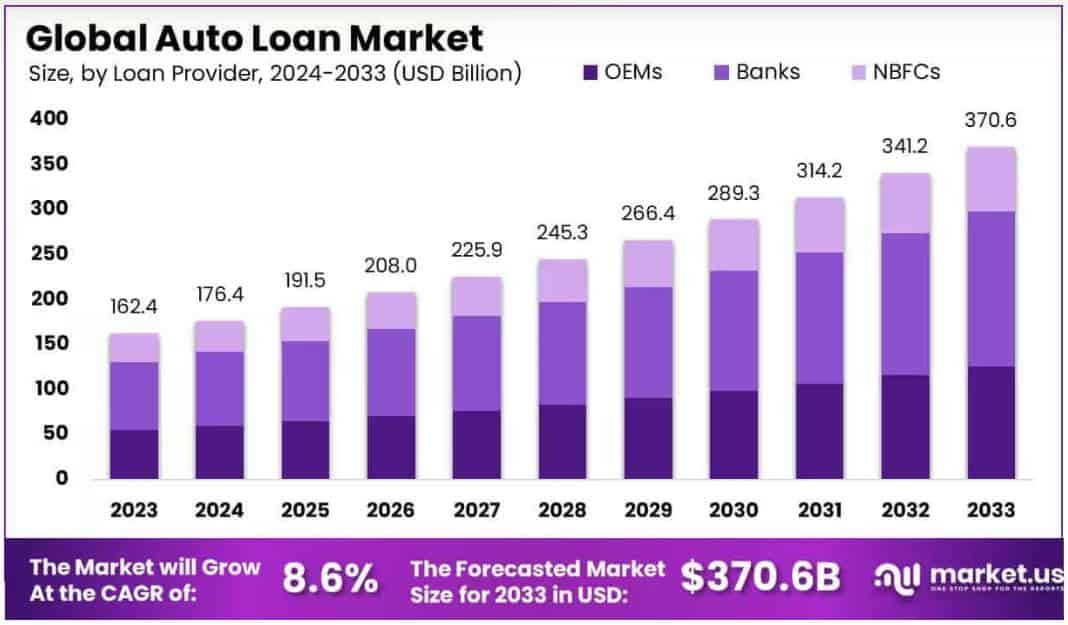
- The global auto loan market is rapidly growing, with the market size expected to expand from USD 162.4 billion in 2023 to around USD 370.6 billion by 2033, reflecting an 8.6% CAGR, driven by rising vehicle prices and increasing reliance on financing.
- The total number of auto loan accounts in the United States remained relatively stable at around 87 million, suggesting a mature market, while total balances nearly reached USD 1.68 trillion before slightly declining at the beginning of 2025.
- The combination of rising vehicle prices and financing costs led to an increase in average loan size, with average balances per person exceeding USD 24,400.
- The auto loan default rate kept deteriorating throughout 2024, hitting a peak of approximately 1.66% in the first quarter of 2025, then showing some early signs of stabilization.
- The auto loan origination trend came back to life with a solid push, as they reached 6.2 million in the fourth quarter of 2024, less than 1% of the total amount of loans granted in the previous year, and this was made possible by lower rates, larger inventories, and the reestablishment of incentives.
- Financing of new cars accounted for 47% of total financed vehicles in Q4 2024, the highest share since the pandemic, while leasing has made a comeback, reaching 26% by Q1 2025.
- Credit pressure continues to grow despite rising demand, as 60+ day delinquencies have surpassed levels seen during the 2009 financial crisis.
- Loan stress in the US is primarily concentrated in the Southern states, with Mississippi leading at 9.8%, followed by Louisiana at 8.4% and Georgia at 7.8%.
- Although the unemployment rate is relatively low, 5.1% of auto loan holders in the U.S. are reported as delinquent, indicating financial difficulties across a broad base.
- The outstanding amount of auto loans fell to $ 1.642 trillion in the first quarter of 2025, a decline seldom seen and often interpreted as a sign of reduced borrowing or loan origination.
- Gen Z has the highest delinquency rate at 7.5%, followed by millennials at 6.9%, even though their average payments are lower.
- Older borrowers are more responsible, with baby boomers showing the lowest delinquency at 1.9%, indicating higher incomes, better credit ratings, and greater financial stability.
Auto Loan Market
(Source: market.us)
- The global automobile loan market is undergoing a period of robust, sustained growth, reflecting increased vehicle demand and a growing number of people taking advantage of financing options.
- Market valuation stands at USD 162.4 billion for 2023, and by 203,3 the market is estimated to exceed USD 370.6 billion.
- The market’s growth will be robust over the forecast period, with a 8.60% compound annual growth rate from 2024 to 2033.
- The key drivers of this growth are rising vehicle prices, deeper penetration of consumer credit, and greater acceptance of flexible financing plans among buyers.
- The North American region was the largest player in the automotive loan market in 2023, accounting for more than 40.2% of total market share and generating USD 65.2 billion in revenue.
- The region’s strong automotive infrastructure, robust credit systems, and high demand for both new and used-vehicle financing all contributed to North American dominance.
Auto Loan Market Trends – Accounts, Balances, Delinquencies, And Write-Offs
(Source: assets.equifax.com)
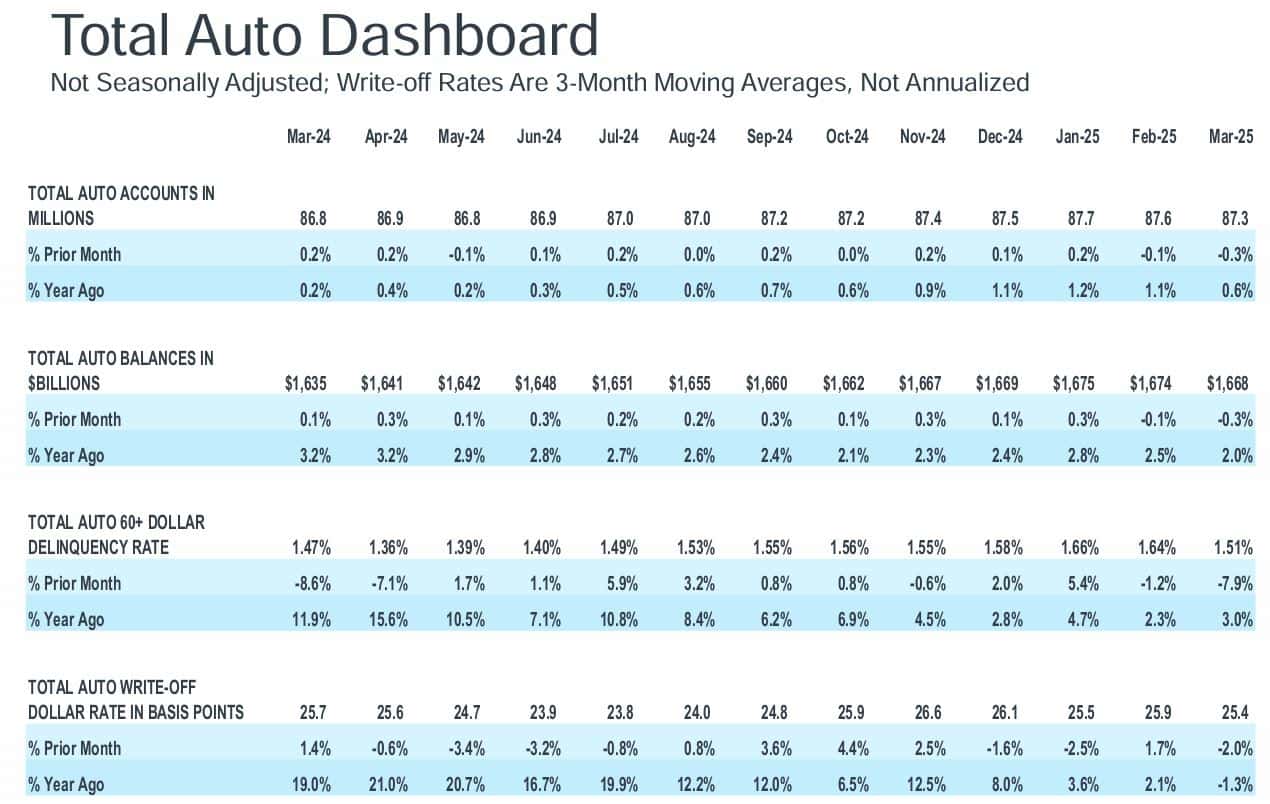
- The provided data portrays a very close and clear view of how the auto loan market changed in the period from March 2024 to March 2025. It includes account volumes, loan balances, delinquency rates, and write-off trends.
- There was not a big difference in the number of total auto loan accounts at the end of 2024 and early 2025, with the number of accounts always being in the range of around 86.8 million to 87.7 million.
- There was a slight month-to-month variation, which is a sign of a mature and steady market with not much increase in the number of borrowers.
- The annual growth rate was the highest around the end of 2024 and the beginning of 2025, which indicates that demand was slightly more than the supply, and then it eased a little bit at the end of March 2025.
- Total auto loan balances rose gradually for most of 202,4, going from about USD 1.64 trillion to an early 2025 peak of around USD 1.68 trillion before slightly going down again in March 2025.
- This increase is attributed to larger loan amounts, likely driven by higher vehicle prices and higher financing costs, despite a flat growth in the number of accounts.
- Auto loan delinquency rates (60+ days past due) deteriorated significantly from the middle to the end of 2024, starting at approximately 1.36%–1.40% and reaching a peak of 1.66% in January 2025.
- This situation indicates that borrowers are experiencing greater repayment stress, likely due to inflation, higher interest rates, or household budget cuts.
- On a positive note, gradually, the number of delinquencies started to decrease by March 2025, which was a sign of the stabilization beginning to take place.
- The rates lenders wrote off as uncollectible also showed the same trend: they declined through mid-2024, then rose sharply and peaked around October— November 2024.
- The implication is that banks had begun to absorb more of the losses on the loans, a trend that had already been underway since the rise in late payments.
- By the beginning of 2025, write-off rates had again declined to a level that was only slightly higher than the observed improvement in delinquency trends.
U.S. Auto Loan Market Shows Growth Momentum Amid Rising Credit Pressure
- The coming of 2025 is heralded by a robust U.S. auto loan market that is strong enough to weather the emerging credit risks, thanks to the gradually improving financing conditions, as highlighted by the data.
- In Q4 2024, auto loan originations reached 6.2 million, which is an 8% increase when compared to the same quarter of the previous year.
- The rise in originations was not limited to certain segments but was universal across different risk levels, with super prime borrowing groups leading the way with a rise of nearly 16% YoY growth.
- The aforementioned factors, such as the Federal Reserve’s rate cuts, increased demand and facilitated customer payments, enabling customers to purchase vehicles through financing.
- In Q4 2024, the share of new vehicles in total financed vehicles was 47% which is the highest percentage of the past pandemic period, and together with other indicators points to the fact that there is a new wave of demand for new cars.
- Leasing, which had been declining in numbers during the pandemic, also saw its share increase to 26% in Q1 2025, gradually approaching pre-pandemic levels.
- Even though the number of total auto loan accounts remained approximately 80 million, the average sizes and payments of the loans still went up.
- The average monthly payment had already reached US$759 for new cars and US$526 for used cars by the end of the period.
- On the other hand, the average loan amount per consumer rose to more than US$24,400, indicating rising car prices and borrowing amounts.
- The delinquency rate of 60+ days past due loans rose to 1.38% in Q1 2025, exceeding the peak observed during the 2009 economic crisis. However, the rate of increase has recently decelerated.
- New-vehicle loan vintages are generally on par with pre-pandemic performance, but default rates are high among prime and subprime borrowers, implying limited affordability in the strongest credit segments.
- In the near term, industry professionals predict that loan volume in Q1 2025 will be even higher, as consumers are expected to accelerate purchases to avoid tariff-related price hikes.
- However, there is a risk that risks will materialise over the long term due to trade policies and ongoing affordability pressures, which may reverse some recent market victories.
State With The Highest Auto Loan Delinquency
(Source: lendingtree.com)
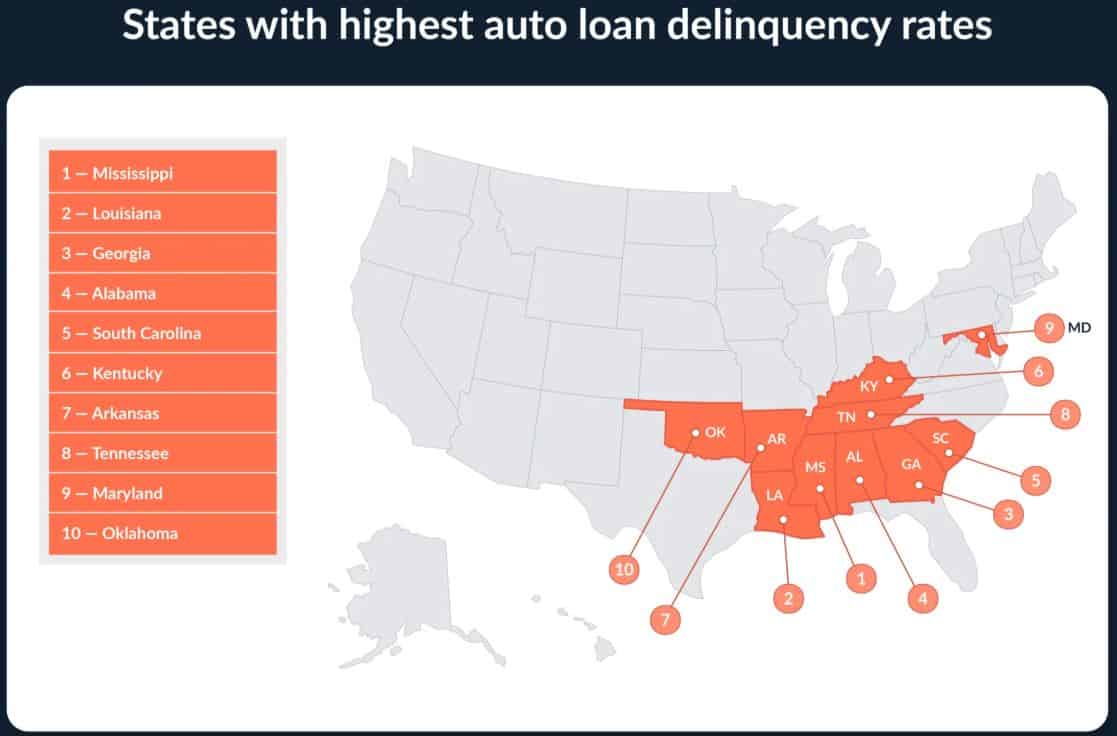
- The study indicates that the stress of auto loan repayment is primarily observed in the southern states of the United States.
- As a matter of fact, the highest rate of auto loan borrowers with at least one delinquent account (9.8%) is reported in Mississippi.
- The second position is taken by Louisiana with an 8.4% delinquency rate, while the third position is held by Georgia with a 7.8% rate, thereby confirming the regional trend.
- A close association between high rates of delinquency and factors such as low household incomes, high inflation sensitivity, and relatively high costs for cars and insurance all characterises the southern states.
- Consumers in these states often use automobile loans to meet transportation needs, thus making them susceptible to economic downturns.
- The statistics not only signify that there is a disparity between the economies of South and North but also that such a disparity has a direct impact on the increasing auto loan delinquency risks in the southern states.
Rising Auto Loan Delinquencies Signal Growing Financial Stress In The U.S.
- The data indicate that the financial burden on U.S. families is getting heavier, as the first quarter of 2025 saw the rate of people with auto loans and at least one delinquent account rise to 5.1%.
- Delinquency rates vary significantly across states, ranging from 3.2% to 9.8%, illustrating the presence of varying economic conditions throughout the U.S.
- These numbers are alarming, as people usually consider car payments as a primary financial obligation, because the lack of transportation is a major reason for losing jobs and, consequently, losing income.
- An increase in auto loan defaults has been identified by experts as a strong signal that many customers are struggling with their financial commitments.
- Persistent inflation, high interest rates, tariff uncertainties, and general economic panic are all contributing to stress on household budgets, even though unemployment remains low.
- At the same time, the distribution of late payments indicates that the pressure is coming from different levels: 2.0% of the borrowers are 30 days or more behind, 0.9% are 60 days late, and another 0.9% are between 90 and 120 days past due, implying that some of the borrowers are seriously struggling.
- Simultaneously, the total amount of auto loans outstanding is starting to decrease. Outstanding auto loan balances dropped to US$1.642 trillion in the first quarter of 2025, a decline of 0.8% from the previous quarter.
Autoloan And Default Statistics By Generation
(Reference: lendingtree.com)
- The analysis reveals that auto loan repayment problems are primarily observed among younger generations, particularly Gen Z and millennials.
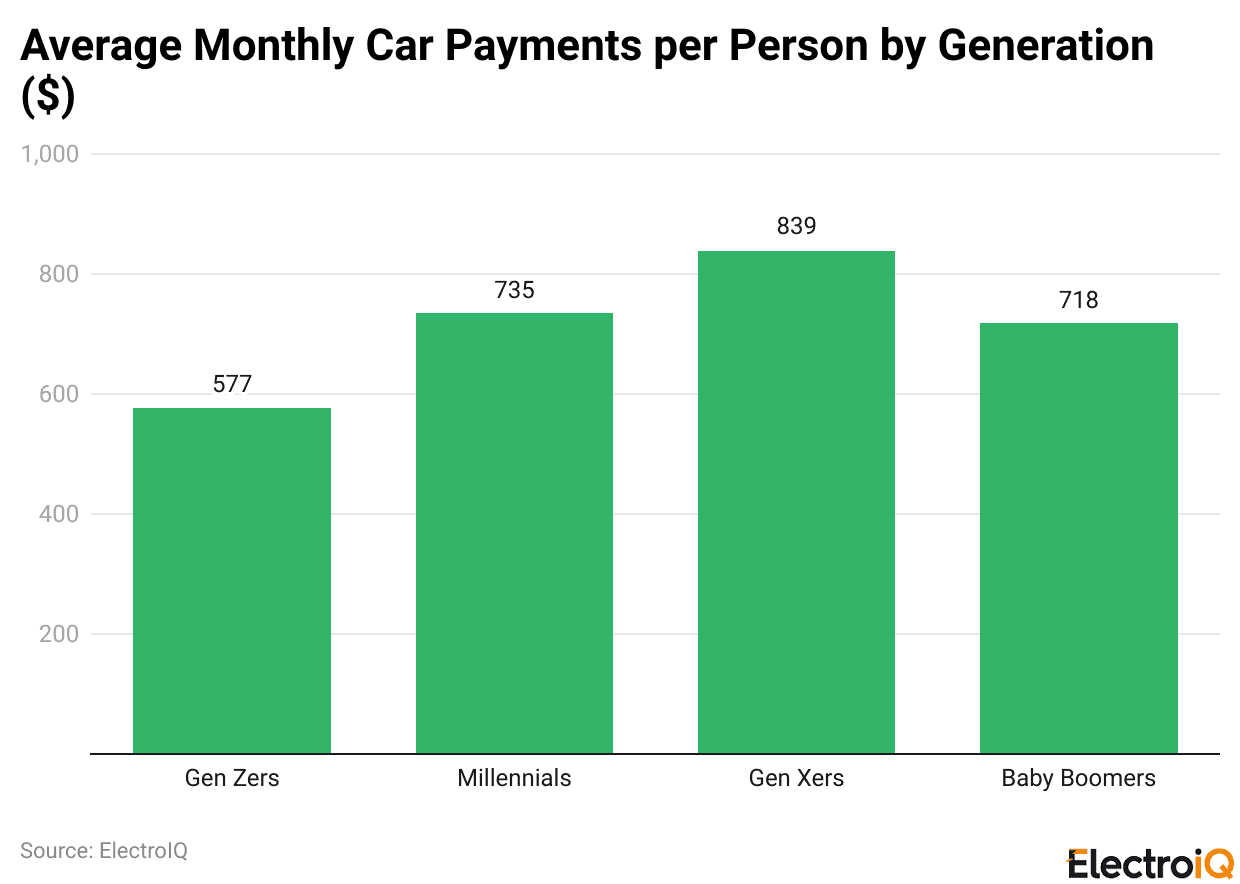
- Gen Z personal loans for borrowers aged 18 to 28 have the highest car credit default rate at 7.5%, but they also have the lowest average monthly payment of US$577.
- This indicates that payment size is not the only factor determining the ability to pay; income and financial stability are far more important.
- Millennials aged 29 to 44 are under considerable pressure, with a 6.9% delinquency rate and average monthly payments of US$735.
- In comparison, the older generations are much more stable financially regarding car loans.
- The baby boomer generation, aged 61-79, has the lowest delinquency rate of just 1.9% and averages monthly payments of US$718, which is still considered a relatively moderate payment.
- Borrowers from Generation X, aged 45-60, have a 4.3% delinquency rate and the highest monthly payments at US$839.
- Experts explain that younger borrowers are at a disadvantage because they typically have lower incomes, less experience with credit management, and, as a result, often have lower credit ratings.
- All these aspects can result in higher interest rates and very tight budgets, making it harder for Gen Z and millennials to keep up with their auto loan payments and leading to defaults, when compared to older generations who are more financially secure.
Conclusion
Auto Loan Performance and Default Statistics: To sum up, the auto loans market of 2025 still exhibits both the sharks’ teeth as well as the naval strength of the latter. The global automotive finance and U.S. lending sectors remain the top performers, generating most of their income from rising vehicle demand and rate cuts. However, rising delinquencies are a clear signal to lenders that borrowers’ financial situation is deteriorating.
Consumers in younger generations and living in lower-income areas, with the South hardest hit, are those most affected by large loan amounts, high monthly payments, and affordability constraints. However, despite the early signs of stabilization, delinquent accounts are still above the historical norms. In the future, the credit risk situation will be determined by the combination of the three factors: economic uncertainty, inflation, or policy change.

